Introduction of Plastic Recycling Machine
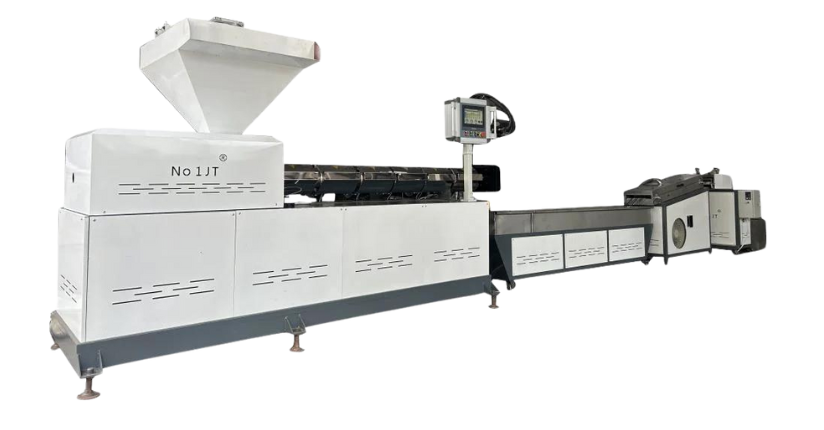
- Definition and Role Plastic recycling machine is a kind of machine and equipment specialized in recycling plastic waste products. It can sort, clean, crush, melt and other processing of various plastic products into reusable plastic raw materials, providing an effective way for the recycling of plastics.
- The importance of recycling plastic Plastic is a durable, lightweight, easy to process materials, widely used in daily life and industrial fields. But at the same time, plastic is also a major solid waste, if not recycled, will bring serious pollution to the environment. Therefore, recycling and reusing plastic waste products is conducive to saving resources, reducing white pollution, protecting the environment and realizing sustainable development.
- Different types of plastic recycling machines
- Single Head Plastic Recycling Machine It is suitable for the recycling of a single type of plastic, such as film, bottles and cans, and other specific plastic varieties. It has a single function but simple structure and low cost.
- Multi-Head Plastic Recycling Machine It can process many different types of plastics at the same time, flexible processing, and wide range of product applications. However, the equipment is more complicated and the price is higher.
- Full-automatic Plastic Recycling Line Integrates feeding, sorting, crushing, washing, dewatering, drying, compaction molding and other processes. High degree of automation, large capacity, but covers a large area, high investment.
- Mobile Plastic Recycling Machine The whole machine adopts trailer or container design, which is convenient for transfer and local recycling. It is suitable for small recycling points or temporary use in construction sites.
Working Principle of Plastic Recycling Machines
- Main Working Process The main working process of plastic recycling machines includes: feeding → sorting → coarse shredding → washing → drying → fine shredding → melting and extruding → pelletizing or molding. Through physical and chemical processing, the recycled plastics are converted into reusable plastic pellets or products.
- Sorting, Washing, Shredding, Melting, etc.
- Sorting: Different types of plastics are separated by manual or automated sorting equipment and fed into different processing lines.
- Coarse Shredding: Large plastic products are mechanically shredded into smaller pieces for easier subsequent processing.
- Washing: Water baths, centrifugal force, etc. are used to remove surface contaminants and foreign matter from the plastics.
- Drying: Hot air or centrifugal force is used to remove moisture from the washed plastic materials.
- Fine Shredding: The dried plastics are further shredded into smaller granular form.
- Melting and Extruding: The plastic granules are melted at a certain temperature and extruded through a die to form pellets or products.
- Differences Between Different Types
- Single and multi-head machines differ in the variety of plastics they can process.
- Fully automated production lines have a high degree of integration but require more auxiliary equipment, such as conveyors and metal separators.
- Mobile units prioritize portability and flexibility, with a compact structure but limited processing capacity.
- Different models may also vary in the specific implementation methods for sorting, shredding, melting, etc.
Selecting Suitable Plastic Recycling Machines
- Assessing Recycling Needs (Types, Quantities, etc.) Before choosing a plastic recycling machine, it’s crucial to evaluate your specific recycling needs. This includes considering the types of plastics you need to recycle (e.g., PET, HDPE, PP, etc.), the expected quantities or volumes, and any specific requirements for the recycled plastic products (e.g., pellets, flakes, or finished goods).
- Machine Capacity and Processing Capability Different plastic recycling machines have varying capacities and processing capabilities. You should consider the throughput rate (e.g., tons/hour or kg/hour) to ensure the machine can handle your desired processing volume. Additionally, assess the machine’s ability to handle different plastic types, sizes, and contaminant levels effectively.
- Budget and Cost Considerations Plastic recycling machines can vary significantly in cost, ranging from small-scale units for modest operations to large-scale, fully automated production lines. Determine your budget and consider not only the initial investment but also ongoing operational costs, such as energy consumption, maintenance, and labor requirements.
- Machine Size and Footprint The physical size and footprint of the recycling machine are important factors, especially if you have limited space available. Compact or mobile units may be more suitable for smaller facilities, while larger plants may require more extensive floor space to accommodate larger machines and supporting equipment.
When evaluating machine options, it’s advisable to consult with experienced suppliers or industry experts. They can provide valuable guidance on matching the right machine specifications to your specific recycling needs, budget, and operational constraints.
Installing and Operating Plastic Recycling Machines
- Site Selection and Preparation Choosing the right location and properly preparing the site are crucial steps before installing a plastic recycling machine. Consider factors such as:
- Accessibility for material delivery and product distribution.
- Adequate space for the machine, ancillary equipment, and material handling.
- Proper ventilation, lighting, and utilities (electricity, water, etc.).
- Floor reinforcement to support the weight of the equipment.
- Compliance with local zoning regulations and environmental requirements.
- Machine Installation and Commissioning Once the site is ready, the next step is the installation and commissioning of the recycling machine. This process typically involves:
- Unloading and positioning the machine components.
- Assembling and connecting various parts and subsystems.
- Installing necessary utilities (power, water, air, etc.).
- Calibrating and testing the machine’s functions.
- Conducting trial runs and making necessary adjustments.
- Operator Training and Safety Precautions Proper operator training is essential for safe and efficient machine operation. This should cover:
- Comprehensive understanding of the machine’s functions and controls.
- Safe operating procedures and emergency protocols.
- Proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Maintenance and troubleshooting procedures.
Safety should be the top priority, with strict adherence to safety guidelines and protocols to prevent accidents, injuries, or equipment damage.
- Maintenance and Care Regular maintenance and care are crucial for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of the plastic recycling machine. This includes:
- Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedules.
- Conducting regular inspections and replacements of worn parts.
- Proper lubrication and cleaning of components.
- Monitoring and maintaining optimal operating conditions.
- Keeping accurate maintenance logs and records.
Proper maintenance not only extends the machine’s lifespan but also helps to ensure consistent product quality and operational efficiency.
Plastic Reuse and Applications
- Uses of Recycled Plastic Pellets The plastic pellets produced from recycling machines can be widely used as raw materials for various applications. Some common uses include:
- Manufacturing new plastic products through injection molding, extrusion, or blow molding processes.
- Producing plastic lumber, furniture, construction materials, and other building products.
- Mixing with virgin plastic resins to create composite materials with desired properties.
- Conversion into plastic films, bags, or packaging materials.
- Use as feedstock for certain chemical processes or energy recovery through incineration.
- Manufacturing Process for New Products To manufacture new products from recycled plastic pellets, the following general process is followed:
- Pellet sorting and blending (if necessary) to achieve desired material properties.
- Drying the pellets to remove moisture and prepare them for processing.
- Melting and plasticizing the pellets using an extruder, injection molding machine, or other processing equipment.
- Forming the molten plastic into the desired shape or product through molding, extrusion, or other forming processes.
- Cooling and solidifying the formed product.
- Additional finishing operations, such as trimming, assembling, or decorating, as required.
- Application Examples and Case Studies Recycled plastics find numerous applications across various industries, including:
- Packaging industry: Bottles, containers, bags, and films.
- Construction: Plastic lumber, pipes, fencing, and landscaping products.
- Automotive: Interior and exterior components, under-the-hood parts.
- Consumer goods: Household items, furniture, toys, and outdoor equipment.
- Textiles: Fiber production for clothing, carpets, and other fabrics.
Case studies and success stories can highlight innovative ways companies have incorporated recycled plastics into their products, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
Development Trends and Prospects for Plastic Recycling
- Policies, Regulations, and Environmental Requirements Governments and regulatory bodies around the world are increasingly implementing policies and regulations aimed at promoting plastic recycling and reducing plastic waste. These include:
- Bans or restrictions on single-use plastics and non-recyclable plastics.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) programs that hold manufacturers accountable for end-of-life product management.
- Landfill and incineration levies or taxes to incentivize recycling over disposal.
- Minimum recycled content requirements for certain plastic products.
- Stricter environmental standards and emissions regulations for recycling facilities.
These policies and regulations are driving the demand for efficient and sustainable plastic recycling solutions.
- Technological Innovations and Automation Upgrades The plastic recycling industry is continuously evolving through technological advancements and automation upgrades, such as:
- Improved sorting and identification technologies (e.g., optical, infrared, and AI-based systems) for better material separation.
- Advanced cleaning and decontamination processes for removing impurities and contaminants more effectively.
- Increased use of robotics and automation in material handling and processing, improving efficiency and safety.
- Development of chemical recycling techniques to break down plastics into their molecular building blocks for reuse.
- Integration of Industry 4.0 concepts, such as Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, and predictive maintenance.
These innovations are enabling more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly plastic recycling processes.
- Industry Status and Market Potential The global plastic recycling industry is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing environmental awareness, regulatory pressures, and the circular economy movement. Key factors shaping the industry include:
- Rising demand for recycled plastic products across various sectors, including packaging, construction, automotive, and consumer goods.
- Expansion of recycling infrastructure and investment in advanced recycling facilities.
- Development of new markets and applications for recycled plastics, such as in the textile and chemical industries.
- Growing consumer preference for sustainable and eco-friendly products, driving demand for recycled materials.
- Opportunities for public-private partnerships and collaboration along the plastic value chain to improve recycling rates and resource efficiency.
However, challenges such as low recycling rates in certain regions, contamination issues, and competition from low-cost virgin plastics remain. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for the continued growth and success of the plastic recycling industry.